| 1950s Highlights |
 July, 1950:
First North American Helicopter Transcontinental Flight July, 1950:
First North American Helicopter Transcontinental Flight
 July 12, 1957:
Dwight Eisenhower became first US President to fly in helicopter July 12, 1957:
Dwight Eisenhower became first US President to fly in helicopter
 Kaman K-225:
First World's turbine gas powered helicopter (1951) Kaman K-225:
First World's turbine gas powered helicopter (1951)
 Sikorsky S-55:
First World's certified commercial transport helicopter (1951) Sikorsky S-55:
First World's certified commercial transport helicopter (1951)
 Sikorsky S-55:
First transatlantic crossing WITH STOPs (1952) Sikorsky S-55:
First transatlantic crossing WITH STOPs (1952)
 McDonnell XV-1:
First successful conversion from vertical rotor lift
to horizontal winged flight (1954) McDonnell XV-1:
First successful conversion from vertical rotor lift
to horizontal winged flight (1954)
 Sud-Aviation SE313B Alouette II:
First turbine helicopter enter production (March 12,1955) Sud-Aviation SE313B Alouette II:
First turbine helicopter enter production (March 12,1955)
 April 27, 1955
Jean Ross Howard Phelan establishes the Whirly Girls
April 27, 1955
Jean Ross Howard Phelan establishes the Whirly Girls
 Kaman QH-43:
First World's remotely piloted rotor vehicle (1957) Kaman QH-43:
First World's remotely piloted rotor vehicle (1957)
 Hiller X-18:
World's first transport-size VTOL aircraft (1959) Hiller X-18:
World's first transport-size VTOL aircraft (1959)
|
 IPD BF-1 Beija Flor : (Brazil)
IPD BF-1 Beija Flor : (Brazil)
Designed by Heinrich Focke. One unit built.
First flight January 1959.
 XE-II (Czechoslovakia)
XE-II (Czechoslovakia)
Their first flying private design, had two-bladed main
and tail rotor and relatively simple construction, consisting of steel tube
framework and tricycle landing gear. Only one flying prototype ( OK-FYA ) was often
updated (modification A through E) and was destroyed during an accident in 1952.
 VZLU HC-2 / HC-102 Heli Baby (Czechoslovakia)
VZLU HC-2 / HC-102 Heli Baby (Czechoslovakia)
After three year of construction (by Mr. Slechta ) this helicopter fly for the
first time in 1954. It was a really good helicopter at that time and set several
international records (120 km/h at closed circuit, 114 km/h at stright line -
27.6.1959).
The serial production started at Moravan Otrokovice factory in 1958
and a small number of HC-2 were delivered to the army.
In 1961 they were returned to the factory and were later converted to HC-102.
 Matra - Cantinieau MC - 101 (France)
Matra - Cantinieau MC - 101 (France)
 Aerotecnica AC-12 / 13 / 14 (France)
Aerotecnica AC-12 / 13 / 14 (France)
Derivate from the MC-101 built in Spain
 Bolkow Bo-46 / 102 / 103 (Germany)
Bolkow Bo-46 / 102 / 103 (Germany)
 Cierva W.14 [Saunders-Roe Saro Skeeter] (UK)
Cierva W.14 [Saunders-Roe Saro Skeeter] (UK)
 Fairey Ultra Light (UK)
Fairey Ultra Light (UK)
 NHI Model 3 Kolibrie (Netherlands)
NHI Model 3 Kolibrie (Netherlands)
 FIAT model 7002 (Italy)
FIAT model 7002 (Italy)
Unique helicopter designed
by this italian company.
It was canceled
 Manzolini Libellula (Italy)
Manzolini Libellula (Italy) not produced
 Aer Lualdi Models L-55/57/59
Aer Lualdi Models L-55/57/59
 PZL BZ-4 (Poland)
PZL BZ-4 (Poland)
 Yakovlev Yak-24 Horse
Yakovlev Yak-24 Horse
This model is the unique tandem-rotors helicopter to enter service in the Soviet Union.
 Apostolescu Universal Helicopter Co. Inc (USA)
Apostolescu Universal Helicopter Co. Inc (USA)
A least-known American inventor and helicopter
pioneer was Stefan Apostolescu, of Rumanian origin.He has been associated with
the rotary-winged industry since early 1940. Several U.S. patents were granted to
him, concerning helicopters, convertiplanes and advanced aircraft systems.
In 1955-1956, Apostolescu set up his own company, the "Apostolescu Universal
Helicopter Co. Inc.", at 55 West 42nd Street, New York, and started the
development of a four-to-five passenger amphibious roadable helicopter, with
collapsible blades, called a "Helimobile" .
The company had plant facilities at Hicksville, Long Island.
Thanks Denes Bernad.
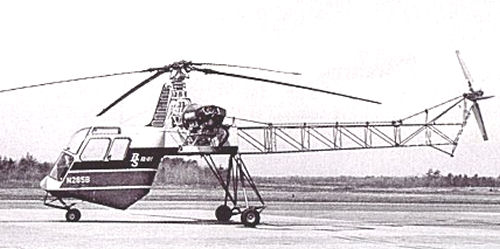
 McCulloch MC-4 (YH-30)
McCulloch MC-4 (YH-30)
Development of the Jov-3
 McCulloch J-2 Gyro Plane
McCulloch J-2 Gyro Plane
 1954, Long Island, New York, USA :
Helicopter Case Baffles Nation
1954, Long Island, New York, USA :
Helicopter Case Baffles Nation
 Transcendental Model 1G
Transcendental Model 1G
 Transcendental Model 2
Transcendental Model 2
An improved (1500 Kgs) successor to the Model 1G, powered by a 250 h.p.
Lycoming 0-435-23 engine mounted behind the cabin and driving two fully
articulated rotors was tested in 1956-57, but the US Air Force decided to
not fund it further in order to pursue the competing Bell XV-3.
A Model 3 has been projected. I will also be
convertible and designed to take two gas-turbines.
 Rotor Craft RH-1
Rotor Craft RH-1 With a max weight of 181 Kg can reach 100 km/h
 De Lackner DH-4 / 5 Aerocycle
De Lackner DH-4 / 5 Aerocycle
Single seat in which the pilot and engine were located in a small
platform above a pair of contra rotating rotors. Below was a
tubular skid landing gear
 American XA-8 [XH-26]
American XA-8 [XH-26]
The US Army and US Air Force jointly evaluated the five XH-26
prototypes from 1952 to 1954. The machines were found to be robust
in construction and relatively simple to operate, but neither service
procured the type in quantity.
American XH-26A Jet Jeep serial number 50-1840
 Detemple DH-28
Detemple DH-28
 Brantly B-2 (YHO-3)
Brantly B-2 (YHO-3)
 Goodyear GA-400R Gizmo
Goodyear GA-400R Gizmo
Well known for its airships, the Goodyear Aircraft Corporation developed a small open-frame single seat helicopter which made its first flight on 9 May 1954. This prototype (N62N) was designated GA-400R Gizmo and followed classic lines with the pilot seat on the forward frame, a narrow tailboom with a tail rotor and the 32hp Mercury 55 engine mounted amidships and driving a two-blade main rotor. It was followed by the GA-400R-2 and GA-400R-3 (N69N and N53A) which were powered by a 38hp Johnson two-stroke engine. Like many contemporary ultra-light helicopters the GA-400R did not progress beyond prototype stage.
 Doman :
Doman : In 1945, Glidden Doman founded the Company.
The first prototype was the LZ-1, a development of the
Sikorsky R-6 that later was improved as LZ-2.
With some of german 's Flettner patents and owns ideas
Doman completely built the LZ-4 and soon
the derivative LZ-5 that was tested by the US Army in 1953 as
YH-31 but was not accepted
Hiller acquired the production rights of the LZ-5 that year
The Company was re founded as Caribe
Doman and his last intents were the D-10 and D-19.
Omega BS-12
Four prototypes tested between 1956 and 1960
 Marquardt Model 14
Marquardt Model 14
 Bensen X-25 Gyro-Copter
Bensen X-25 Gyro-Copter
In the early '50s, Igor Bensen, an engineer who
works for Kaman Aircraft, founded his own company. He made the
kit B-8 Gyro-Glider that it can be "made by yourself" .
For more than 30 years, thousands of this machines were
produced. Other models were the B-9 Little Zipter and the B-10
Flying Platform
 Doak Model 16 (VZ-4)
Doak Model 16 (VZ-4)
Experimental tiltrotor for the US Army. Only one built and tested until 1963
when the program was cancelled and transferred to NASA.
In 1973 was put in storage at Fort Eustis, VA and then restored for display
at the e US Army Transportation Museum
 Seibel S-4 Sky-Hawk (YH-24)
Seibel S-4 Sky-Hawk (YH-24)
Was not selected by the US Army but later, in 1951, received civilian certification.
Charles Seibel began his helicopter career at Bell buffalo, then began his own company in
Wichita, Kansas and sold it out to Cessna in 1952. He became chief engineer of the
Cessna Helicopter Division and was responsible for the development of the remarkable Cessna CH-1 design
 Cessna CH-1 Skyhook ( YH-41 Seneca )
Cessna CH-1 Skyhook ( YH-41 Seneca )
Cessna entered the helicopter market following its
acquisition of the Seibel Helicopter Company in 1952
In the summer of 1959, the CAA ( predecessor of today's FAA ) approved the CH-1C for certification and after a few minor additional modifications, the CH-1C became the first helicopter CAA-certified for flight in instrument conditions.
 Ryan Model 92 Vertiplane (VZ-3)
Ryan Model 92 Vertiplane (VZ-3)
Experimental Tiltrotor built for the US Army. First flew December 29, 1958
and completed 21 flights until it crashed in 1959. Repaired and handed over to NASA.
Currently on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum.
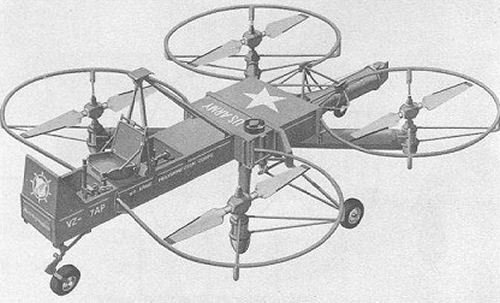
 Curtiss-Wright Aerial Jeep (VZ-7)
Curtiss-Wright Aerial Jeep (VZ-7)
Flying test vehicle, serial number 58-5508 currently
at US Army Aviation Museum in Fort Rucker, Alabama
 Kellett / Hughes XH-15 / XH-17
Kellett / Hughes XH-15 / XH-17
|
|
Helicopters for sale
Accidents
Acronyms
Airshows
Future helicopters
Flying a helicopter
Helicopter stories
TV and movies
Helicopter books
Helicopter patches
Helicopter model kits

|