Developed from the YHC-1A (which eventually became the CH-46)
at the end of the 1950s, the Chinook is the longest running continual production program
in The Boeing Company.
The Boeing Chinook is a tandem rotor, heavy-lift helicopter that
meets tactical and combat support mission requirements for military forces around the world. The Chinook
is one of the world’s most reliable and efficient transport helicopter, capable of handling loads up to 28,000
lbs with a maximum gross weight of 54,000 lbs. (24,494 kg), greater than its own empty weight.
Its tandem rotor configuration also provides exceptional handling qualities that enable the CH-47 to
operate in climatic, altitude and crosswind conditions that typically keep other helicopters from flying.
The first fully equipped U.S. Army Chinook designated the CH-47A completed first flight Sep 21th 1961 and entered service in August 1962 with a gross weight of 33,000 lbs. (14,969 kg).
Boeing Vertol introduced the CH-47B in 1966 with an improved airframe and power plant provided by the T55-l-7C engines. The gross weight rose to 40,000 lbs. (18,144 kg).


The CH-47C was developed in 1967 in response to the U.S. Army’s request for transporting a 15,000 lb. (6,804 kg) payload a distance of 30 nm (56 km) radius on a 95oF (35oC) day at 4000 ft. (1,219 m). Powered by T55-l-11 engines and had a gross weight capability of 46,000 lbs. (20,865 kg).
The Chinook was also produced in Italy by Meriodionali SpA and in Japan by kawasaki heavy industries.
The next CH-47D Large external- and internal- load capabilities and high airspeeds allow them to do the work of three utility helicopters, and give it the lowest cost-per-ton-nautical-mile of any U.S. Army helicopter. The CH-47D’s cabin measures 30 x 8.3 x 6.5 feet (9.14 x 2.53 x 1.98m). It’s big enough to lift two HMMWVs or a HMMWV plus a 105-mm howitzer and gun crew, yet its fuselage is only 12 inches (30.5 cm) longer than the Army’s UH-60 Black Hawk utility helicopter.
1964 - CH-47A
2011 - CH-47F

Under the 2005 contract, the US Army will modernize its entire fleet of 397 CH-47D Chinooks to the new F-model configuration and procure at least 55 additional new-build CH-47F Chinooks. The U.S. Army Special Operation Command will increase its inventory of 34 MH-47D/E Special Operations Heavy Assault Chinooks to 61 MH-47Gs, with an option for future growth.
The MH-47G is the Special Operations variant first delivered in 2004. Required to complete long-range missions at low level, day or night, in adverse weather, over any types of terrain, the MH-47G’s fully integrated digital Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS) permits global communications and navigation. CAAS is among the most advanced U.S. Army helicopter systems, soon to be installed in U.S. Army Special Operations Command’s MH-60 and A/MH-6 helicopters. CAAS includes integrating forward-looking infrared (FLIR) and multimode radar for nap-of-the-earth and low-level flight operations in conditions of extremely poor visibility and adverse weather. Today’s MH-47Gs contain fully integrated, digital cockpit management system, long-range fuel tanks and advanced cargo-handling capabilities that complement the aircraft’s mission performance and handling characteristics.
The MH-47G combines many proven Chinook systems and features. Notable among these are fuel tanks providing twice the capacity of the CH-47F and an in-flight refueling system. MH-47Gs are remanufactured on the CH-47F production line, with most G-model systems installed during the final stages of completion. Also, rescue hoist, fast rope, multi-mode radar and Forward Looking Infrared Radar.
61 MH-47Gs are currently required for 160th SOAR.
On Nov 9, 2006 Boeing 's HH-47 was awarded the U.S. Air Force Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR-X) Contract
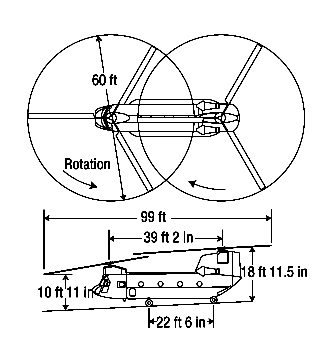
- Length: Fuselage 52.0 ft. (15.9 m) Incl. Rotors 99.0 ft. (30.18 m)
- Width: 12.42 ft (3,78 m) 15.75 ft (4.8 m)
- Rotor Diameter: 60 ft. (18.29 m)
- Height: 18.92 ft. (5.77 m)
- Propulsion: 2 Honeywell 55-GA-714A engines, 4,733 shp (3,529 kW) each
- Speed: 155 kt (287 km/h)
- Fuel: F 1,068 gal. (4,043 L) G/SD 2,068 gal. (7,827 L)
- Useful Load: F 25,000 lbs. (11, 3650 kg) G/SD - 28,537 (12,943 kg)
- Mission Radius: F 200 nm (370.4 km) G/SD - 400 nm (740.8 km)
- Max Gross Weight: F 50,000 lbs. (22,730 kg) G - 54,000 lbs. (24,493 kg)
- Mission: Transport of troops, artillery, ammunition, fuel, supplies, water in support of combat operations, and civil and humanitarian relief
- First Flight: CH-47F June 25, 2001, SD August 25, 1999
CH-47C
On December 15th, 2006, Boeing transfered the Type Certificate for the civilian models Vertol 107 and 234 to Columbia Helicopters which basically now makes Columbia the type design holder (owner). Columbia can now manufacture all parts up to and including the aircraft if they so desire in the future (after issuance by the Federal Aviation Administration FAA of a Production Certificate).
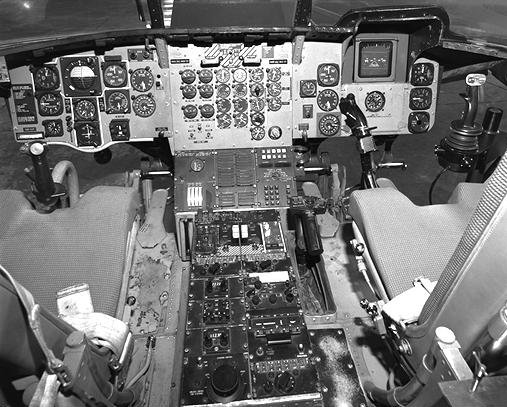 1960s CH-47B panel (NASA photo)
1960s CH-47B panel (NASA photo)
 Armed Chinook variant in Vietnam. Guns A Go-Go
Armed Chinook variant in Vietnam. Guns A Go-Go
 1980s Argentine Army CH-47C variant
1980s Argentine Army CH-47C variant
 1990s CH-47D gets into a C-17 transport aircraft
1990s CH-47D gets into a C-17 transport aircraft
 2006 HH-47 CSAR-X programme winner
2006 HH-47 CSAR-X programme winner
Database:
 Boeing Vertol 114
Boeing Vertol 114
 CH-47 A/B/C
CH-47 A/B/C
 Boeing 414 / CH-47 D/SD
Boeing 414 / CH-47 D/SD
 CH-47 F/G/H
CH-47 F/G/H
The first fully equipped U.S. Army Chinook designated the CH-47A completed first flight Sep 21th 1961 and entered service in August 1962 with a gross weight of 33,000 lbs. (14,969 kg).
Boeing Vertol introduced the CH-47B in 1966 with an improved airframe and power plant provided by the T55-l-7C engines. The gross weight rose to 40,000 lbs. (18,144 kg).


The CH-47C was developed in 1967 in response to the U.S. Army’s request for transporting a 15,000 lb. (6,804 kg) payload a distance of 30 nm (56 km) radius on a 95oF (35oC) day at 4000 ft. (1,219 m). Powered by T55-l-11 engines and had a gross weight capability of 46,000 lbs. (20,865 kg).
The Chinook was also produced in Italy by Meriodionali SpA and in Japan by kawasaki heavy industries.
The next CH-47D Large external- and internal- load capabilities and high airspeeds allow them to do the work of three utility helicopters, and give it the lowest cost-per-ton-nautical-mile of any U.S. Army helicopter. The CH-47D’s cabin measures 30 x 8.3 x 6.5 feet (9.14 x 2.53 x 1.98m). It’s big enough to lift two HMMWVs or a HMMWV plus a 105-mm howitzer and gun crew, yet its fuselage is only 12 inches (30.5 cm) longer than the Army’s UH-60 Black Hawk utility helicopter.
1964 - CH-47A
2011 - CH-47F
Special Operations Chinook
In 1995 Boeing completed delivery of a single MH-47E prototype and 25 production aircraft to the U.S. Army 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment (Airborne), based at Fort Campbell, Ky., and Hunter Army Airfield, Savannah, Ga. This fleet has operated around the world and conducted combat missions in every climate and condition. Training and operational missions accounted for the loss of three MH-47Es since fielding.
Current Versions
Under the U.S. Army Modernization Program, CH-47Ds will be upgraded to Remanufactured CH-47F aircraft. New-Build CH-47F begin deliveries in 2006. CH-47F contains a fully integrated, digital cockpit management system, long-range fuel tanks and advanced cargo-handling capabilities that complement the aircraft’s mission performance and handling characteristics. The CH-47F’s triple-hook system stabilizes large external loads, such as 1550mm howitzers, allowing them to be carried at speeds up to 140 knots (260 km/hr) - or twice as fast as single-suspension loads. Multiple external loads (fuel blivets for example) can be delivered to three separate destinations in a single sortie.Under the 2005 contract, the US Army will modernize its entire fleet of 397 CH-47D Chinooks to the new F-model configuration and procure at least 55 additional new-build CH-47F Chinooks. The U.S. Army Special Operation Command will increase its inventory of 34 MH-47D/E Special Operations Heavy Assault Chinooks to 61 MH-47Gs, with an option for future growth.
The MH-47G is the Special Operations variant first delivered in 2004. Required to complete long-range missions at low level, day or night, in adverse weather, over any types of terrain, the MH-47G’s fully integrated digital Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS) permits global communications and navigation. CAAS is among the most advanced U.S. Army helicopter systems, soon to be installed in U.S. Army Special Operations Command’s MH-60 and A/MH-6 helicopters. CAAS includes integrating forward-looking infrared (FLIR) and multimode radar for nap-of-the-earth and low-level flight operations in conditions of extremely poor visibility and adverse weather. Today’s MH-47Gs contain fully integrated, digital cockpit management system, long-range fuel tanks and advanced cargo-handling capabilities that complement the aircraft’s mission performance and handling characteristics.
The MH-47G combines many proven Chinook systems and features. Notable among these are fuel tanks providing twice the capacity of the CH-47F and an in-flight refueling system. MH-47Gs are remanufactured on the CH-47F production line, with most G-model systems installed during the final stages of completion. Also, rescue hoist, fast rope, multi-mode radar and Forward Looking Infrared Radar.
61 MH-47Gs are currently required for 160th SOAR.
On Nov 9, 2006 Boeing 's HH-47 was awarded the U.S. Air Force Combat Search and Rescue (CSAR-X) Contract
General Characteristics CH-47F
- Length: Fuselage 52.0 ft. (15.9 m) Incl. Rotors 99.0 ft. (30.18 m)
- Width: 12.42 ft (3,78 m) 15.75 ft (4.8 m)
- Rotor Diameter: 60 ft. (18.29 m)
- Height: 18.92 ft. (5.77 m)
- Propulsion: 2 Honeywell 55-GA-714A engines, 4,733 shp (3,529 kW) each
- Speed: 155 kt (287 km/h)
- Fuel: F 1,068 gal. (4,043 L) G/SD 2,068 gal. (7,827 L)
- Useful Load: F 25,000 lbs. (11, 3650 kg) G/SD - 28,537 (12,943 kg)
- Mission Radius: F 200 nm (370.4 km) G/SD - 400 nm (740.8 km)
- Max Gross Weight: F 50,000 lbs. (22,730 kg) G - 54,000 lbs. (24,493 kg)
- Mission: Transport of troops, artillery, ammunition, fuel, supplies, water in support of combat operations, and civil and humanitarian relief
- First Flight: CH-47F June 25, 2001, SD August 25, 1999

CH-47C
On December 15th, 2006, Boeing transfered the Type Certificate for the civilian models Vertol 107 and 234 to Columbia Helicopters which basically now makes Columbia the type design holder (owner). Columbia can now manufacture all parts up to and including the aircraft if they so desire in the future (after issuance by the Federal Aviation Administration FAA of a Production Certificate).
 1960s CH-47B panel (NASA photo)
1960s CH-47B panel (NASA photo)
 Armed Chinook variant in Vietnam. Guns A Go-Go
Armed Chinook variant in Vietnam. Guns A Go-Go
 1980s Argentine Army CH-47C variant
1980s Argentine Army CH-47C variant
 1990s CH-47D gets into a C-17 transport aircraft
1990s CH-47D gets into a C-17 transport aircraft
 2006 HH-47 CSAR-X programme winner
2006 HH-47 CSAR-X programme winner
Database:
