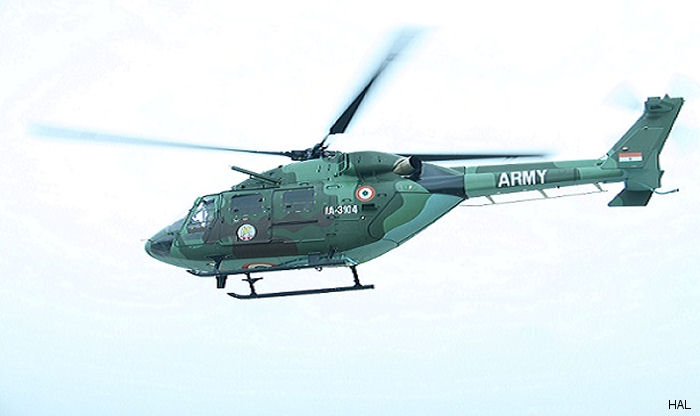
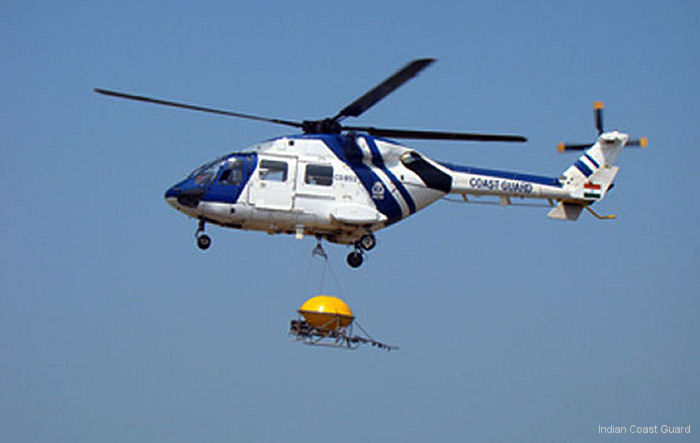
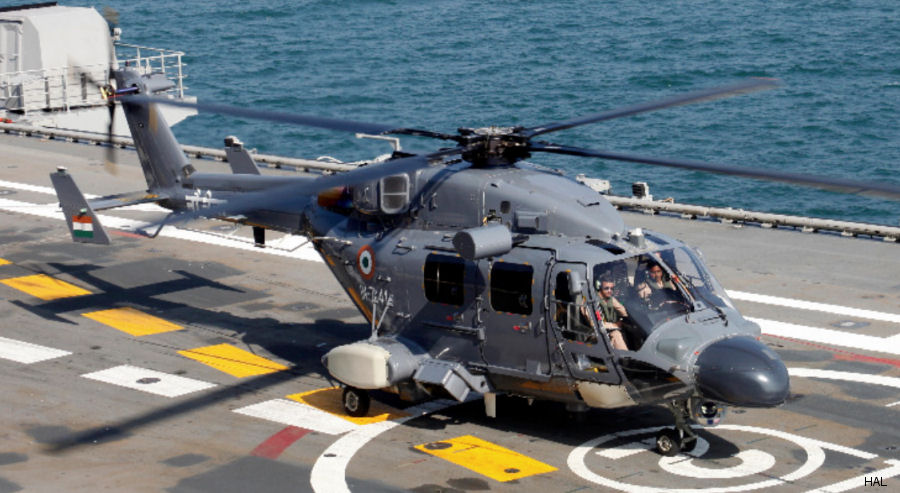
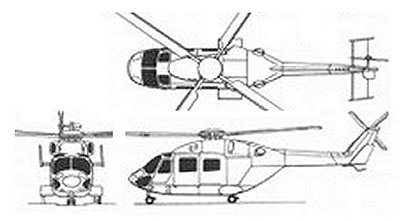
Developed with German ( MBB / Eurocopter) design assistance, the multirole ALH (Advanced Light Helicopter) first flew August 20, 1992. A skid-gear Army/Air Force prototype followed in May 1994 and the wheeled-gear Naval prototype in December 1995.
The first production contract was announced in 1997 for 12 aircraft (Indian Army and Air Force four each, Navy and Coast Guard two each) with deliveries to start next year. Eventual requirements are 110, 150, and 40, respectively, to replace such elderly types as the Cheetah and Chetak.
In March 2002 HAL delivered its first advanced light helicopter to the Coast Guard, ten years after the prototype made its maiden flight. The helicopters cost 5.1 million dollars each.
On February 2004 HAL signed a $33 million contract with Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI) for the supply of entire avionics packages for both domestic and export markets. This ensures that all future production of the Dhruv will feature only Israeli avionics. The first Israeli-supplied avionics will fly on the Dhruv in January 2006. The avionics systems initially will be supplied for 100 helicopters, primarily for the Indian military market. About 300 helicopters eventually will be equipped with the IAI systems. The systems include electronic warfare packages, a day-and-night vision system, head-up display and communication systems.
By March 2004, about 40 Dhruvs were supplied to the three services and the Coast Guard. These helicopters were equipped with indigenously developed avionics systems, supplied by HAL's avionics division and will not receive the Israeli avionics upgrade. The decision to use Israeli avionics was based on recommendations from the Army and Navy. The Navy, in its recommendations submitted to the MoD, requested IAI-built multipurpose surveillance radar and infra-red systems. However the indigenously developed SV-2000 maritime patrol radar will fill in the vital gap of surveillance and a FLIR turret will be acquired from either France or Israel.
Variants
- Dhruv Mk.I : serial production launched in 2001. TM-333-2B2 engine
- Dhruv Mk.II : Launched 2007, has an IAI glass cockpit
- ALH Mk.III : Launched 2012, ALH with Shakti engines and EW systems
- ALH Mk.IV Rudra : Armed variant with a Weapons System Integrated (WSI)
The first production contract was announced in 1997 for 12 aircraft (Indian Army and Air Force four each, Navy and Coast Guard two each) with deliveries to start next year. Eventual requirements are 110, 150, and 40, respectively, to replace such elderly types as the Cheetah and Chetak.
In March 2002 HAL delivered its first advanced light helicopter to the Coast Guard, ten years after the prototype made its maiden flight. The helicopters cost 5.1 million dollars each.
On February 2004 HAL signed a $33 million contract with Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI) for the supply of entire avionics packages for both domestic and export markets. This ensures that all future production of the Dhruv will feature only Israeli avionics. The first Israeli-supplied avionics will fly on the Dhruv in January 2006. The avionics systems initially will be supplied for 100 helicopters, primarily for the Indian military market. About 300 helicopters eventually will be equipped with the IAI systems. The systems include electronic warfare packages, a day-and-night vision system, head-up display and communication systems.
By March 2004, about 40 Dhruvs were supplied to the three services and the Coast Guard. These helicopters were equipped with indigenously developed avionics systems, supplied by HAL's avionics division and will not receive the Israeli avionics upgrade. The decision to use Israeli avionics was based on recommendations from the Army and Navy. The Navy, in its recommendations submitted to the MoD, requested IAI-built multipurpose surveillance radar and infra-red systems. However the indigenously developed SV-2000 maritime patrol radar will fill in the vital gap of surveillance and a FLIR turret will be acquired from either France or Israel.
Variants
- Dhruv Mk.I : serial production launched in 2001. TM-333-2B2 engine
- Dhruv Mk.II : Launched 2007, has an IAI glass cockpit
- ALH Mk.III : Launched 2012, ALH with Shakti engines and EW systems
- ALH Mk.IV Rudra : Armed variant with a Weapons System Integrated (WSI)
Specifications Dhruv |
Derivatives & Versions of Dhruv |
| Model | Year | History |
|---|---|---|
| ALH Rudra 2007 | 2007 | ALH Mk.IV armed version of the Dhruv |
| 2010 | 2010 | India's LCH is a twin-engine, 5.8-ton class helicopter featuring narrow fuselage and tandem configuration for Pilot and Co-pilot/Weapon System Op ... |
List of Operators of Dhruv |
| Years | Model | Org | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002- | | ||||||
| 2002- | | ||||||
| 2002- | | ||||||
| 2005- | | ||||||
| 2009/15 | | ||||||
| 2013- | | ||||||
| | | ||||||
Global Distribution of Dhruv |
|