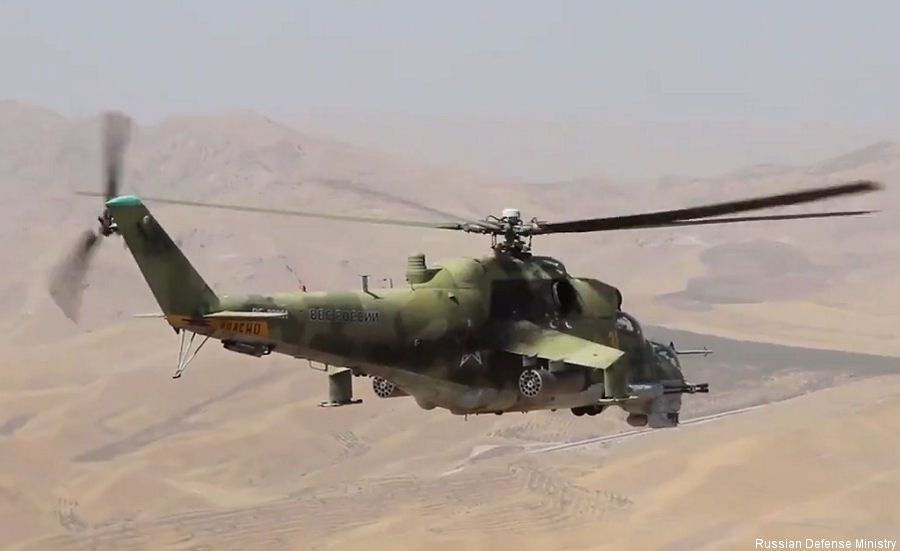
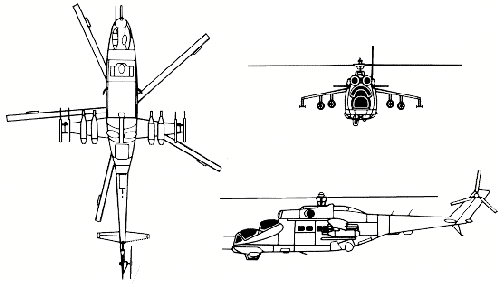
The Mil Mi-24 Hind Flying Tank is a large helicopter gunship and attack helicopter with a troop transport capacity in service since 1972.
In the 1960s, while the western countries were using the helicopter mainly as a transport and rescue machine, the Soviet Army look at them as the air counterpart of the battle tanks. Heavy armed versions of the Mi-8 Hip were in service in those years when the Mil bureau start working in a new prototype called A-10. This new helicopter, which first flew on 19 September 1969, was developed from the beginning as an antitank weapon. The A-10 reached a speed record of 368 km/h. First units were deployed in East-Germany in 1972.
The first versions used a standard helo cockpit with pilots side-by-side, but in 1975 appeared the Hind-D with the now traditional attack cockpit in a tandem configuration Later versions, as the Hind-E, used the more sophisticated AT-6 Spiral missiles instead of the AT-2 Swatter and a 23 mm cannon replacing the 12,7 mm machine gun in the nose mounted turret. In their better moment, more than 1000 Hinds were in service in the Red Army and they were extensively used in Afghanistan where they teamed with the attack aircraft Sukhoi Su-25 Frogfoot.
Produced by the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant is, or was, in use by more than 30 nations. Export variants named Mi-35
 The Mi-24 "Hollywood" variant
The Mi-24 "Hollywood" variant
 US Navy SH-2F Seasprite "Seasnake Two Zero"
getting chased on final approach to landing by a Soviet Frontal Aviation Mi-24D Hind.
Photo taken April 1985 near the La Perouse Straits (between Sakhalin Island and Vladivostok)
- Thanks Gordon!
US Navy SH-2F Seasprite "Seasnake Two Zero"
getting chased on final approach to landing by a Soviet Frontal Aviation Mi-24D Hind.
Photo taken April 1985 near the La Perouse Straits (between Sakhalin Island and Vladivostok)
- Thanks Gordon!
In the 1960s, while the western countries were using the helicopter mainly as a transport and rescue machine, the Soviet Army look at them as the air counterpart of the battle tanks. Heavy armed versions of the Mi-8 Hip were in service in those years when the Mil bureau start working in a new prototype called A-10. This new helicopter, which first flew on 19 September 1969, was developed from the beginning as an antitank weapon. The A-10 reached a speed record of 368 km/h. First units were deployed in East-Germany in 1972.
The first versions used a standard helo cockpit with pilots side-by-side, but in 1975 appeared the Hind-D with the now traditional attack cockpit in a tandem configuration Later versions, as the Hind-E, used the more sophisticated AT-6 Spiral missiles instead of the AT-2 Swatter and a 23 mm cannon replacing the 12,7 mm machine gun in the nose mounted turret. In their better moment, more than 1000 Hinds were in service in the Red Army and they were extensively used in Afghanistan where they teamed with the attack aircraft Sukhoi Su-25 Frogfoot.
Produced by the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant is, or was, in use by more than 30 nations. Export variants named Mi-35
 The Mi-24 "Hollywood" variant
The Mi-24 "Hollywood" variant
 US Navy SH-2F Seasprite "Seasnake Two Zero"
getting chased on final approach to landing by a Soviet Frontal Aviation Mi-24D Hind.
Photo taken April 1985 near the La Perouse Straits (between Sakhalin Island and Vladivostok)
- Thanks Gordon!
US Navy SH-2F Seasprite "Seasnake Two Zero"
getting chased on final approach to landing by a Soviet Frontal Aviation Mi-24D Hind.
Photo taken April 1985 near the La Perouse Straits (between Sakhalin Island and Vladivostok)
- Thanks Gordon!
Specifications Mi-24 Hind |
Derivatives & Versions of Mi-24 Hind |
| Model | Year | History |
|---|---|---|
| Mi-24A | ||
| mi-24du | ||
| mi-24k | ||
| mi-24p | ||
| mi-24rch | ||
| mi-25 | mi-25 is export version of mi-24d | |
| Mi-35 Hind | mi-35 is export version of mi-24v | |
| Mi-35M Hind | Export all weather attack version fitted with advanced avionics including night vision systems | |
| Mi-35P Hind | Export version of Mi-24P | |
| mi-24d 1973 | 1973 | |
| Mi-24V Hind 1975 | 1975 | The Hind-D entered production in 1976 althought was first seen by the west in the early 1980s. Main difference with previous models were four ou ... |